Do Fallen Arches Require Surgery?
Overview

Flat feet can also develop as an adult ("adult acquired flatfoot") due to injury, illness, unusual or prolonged stress to the foot, faulty biomechanics or as part of the normal aging process. This is most common in women over 40 years of age. Known risk factors include obesity, hypertension and diabetes.Flat feet can also occur in pregnant women as a result of temporary changes, due to increased elastin (elasticity) during pregnancy. However, if developed by adulthood, flat feet generally remain flat permanently.
Causes
There is a lack of normal arch development, probably due to inherent ligamentous laxity. Around 20% of adults have Pes planus. The majority have a flexible flat foot and no symptoms. However, if there is also heel cord contracture, there may be symptoms (see 'Contributing factors', below). Loss of support for the arch. Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon, a common and important cause. Tear of the spring ligament (rare). Tibialis anterior rupture (rare). A neuropathic foot, e.g from diabetes, polio, or other neuropathies. Degenerative changes in foot and ankle joints. Inflammatory arthropathy, eg rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis. Fractures. Bony abnormalities, eg tarsal coalition.
Symptoms
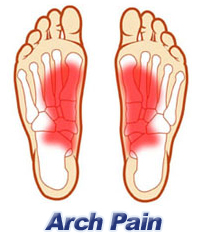
Fallen arches may induce pain in the heel, the inside of the arch, the ankle, and may even extend up the body into the leg (shin splints), knee, lower back and hip. You may also experience inflammation (swelling, redness, heat and pain) along the inside of the ankle (along the posterior tibial tendon). Additionally, you may notice some changes in the way your foot looks. Your ankle may begin to turn inward (pronate), causing the bottom of your heel to tilt outward. Other secondary symptoms may also show up as the condition progresses, such as hammertoes or bunions. You may also want to check your footprint after you step out of the shower. (It helps if you pretend you?re in a mystery novel, and you?re leaving wet, footprinty clues that will help crack the case.) Normally, you can see a clear imprint of the front of your foot (the ball and the toes) the heel, and the outside edge of your foot. There should be a gap (i.e. no footprinting) along the inside where your arches are. If your foot is flat, it?ll probably leave an imprint of the full bottom of your foot-no gap to be had. Your shoes may also be affected: because the ankle tilts somewhat with this condition, the heel of your shoes may become more worn on one side than another.
Diagnosis
Runners are often advised to get a gait analysis to determine what type of foot they have and so what kind of running shoe they require. This shouldn?t stop at runners. Anyone that plays sports could benefit from this assessment. Sports shoes such as football boots, astro trainers and squash trainers often have very poor arch support and so for the 60-80% of us who do overpronate or have flat feet they are left unsupported. A change of footwear or the insertion of arch support insoles or orthotics can make a massive difference to your risk of injury, to general aches and pains and even to your performance.
heelsncleavage
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have flat feet you may not necessarily need treatment -- sometimes a child or even an adult will have low arches and have no problems. It's normal for a baby's or young child's feet to appear flat until the structure of their feet is more fully developed. If flat feet are contributing to secondary problems, especially leg or foot pain, treatment may be necessary. Flat feet can sometimes cause difficulty walking or running and interfere with athletic activities. A visit to a podiatrist will involve an evaluation of foot structure and function. Besides a foot exam, a visit may include foot X-rays and an analysis of your feet while walking. Your podiatrist may prescribe arch supports or orthotics to control the pronation. While orthotics and arch supports don't permanently correct the shape of the arch, they do help control excess pronation that may be causing wear-and-tear on your muscles and joints. Sneakers with a design called motion control are also helpful for overpronators. This style of sneaker has a design that creates more stability by limiting movement in the heel and arch area of the shoe. Additionally, physical therapy and stretching exercises may be in order, especially if tendonitis (tendon inflammation) is present. Flat feet that are the result of congenital or developmental abnormalities may require further intervention, such as bracing, casting or surgical correction. A brace incorporates an arch support into a device that attaches to the lower leg, giving extra support and flat-foot control. Bracing or foot surgery may also be warranted in cases when flat feet are caused by neurological diseases or are aggravated by posterior tibial tendonitis, which can be a long-term complication of flat feet. Casting is a method used for children whose flat feet are caused by bone positional abnormalities, such as metatarsus adductus. It involves using a series of casts to assist in re-aligning leg and foot bones to their proper anatomical position.
Surgical Treatment

Surgical procedures for flat feet vary depending on the root cause of the condition. Surgical correction to control pronation may include bone implants or Achilles tendon lengthening. Tendon transfer, which is a procedure to re-attach a tendon to another area of bone, may also be used to reduce pronation and improve foot function.

Flat feet can also develop as an adult ("adult acquired flatfoot") due to injury, illness, unusual or prolonged stress to the foot, faulty biomechanics or as part of the normal aging process. This is most common in women over 40 years of age. Known risk factors include obesity, hypertension and diabetes.Flat feet can also occur in pregnant women as a result of temporary changes, due to increased elastin (elasticity) during pregnancy. However, if developed by adulthood, flat feet generally remain flat permanently.
Causes
There is a lack of normal arch development, probably due to inherent ligamentous laxity. Around 20% of adults have Pes planus. The majority have a flexible flat foot and no symptoms. However, if there is also heel cord contracture, there may be symptoms (see 'Contributing factors', below). Loss of support for the arch. Dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon, a common and important cause. Tear of the spring ligament (rare). Tibialis anterior rupture (rare). A neuropathic foot, e.g from diabetes, polio, or other neuropathies. Degenerative changes in foot and ankle joints. Inflammatory arthropathy, eg rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis. Fractures. Bony abnormalities, eg tarsal coalition.
Symptoms
Fallen arches may induce pain in the heel, the inside of the arch, the ankle, and may even extend up the body into the leg (shin splints), knee, lower back and hip. You may also experience inflammation (swelling, redness, heat and pain) along the inside of the ankle (along the posterior tibial tendon). Additionally, you may notice some changes in the way your foot looks. Your ankle may begin to turn inward (pronate), causing the bottom of your heel to tilt outward. Other secondary symptoms may also show up as the condition progresses, such as hammertoes or bunions. You may also want to check your footprint after you step out of the shower. (It helps if you pretend you?re in a mystery novel, and you?re leaving wet, footprinty clues that will help crack the case.) Normally, you can see a clear imprint of the front of your foot (the ball and the toes) the heel, and the outside edge of your foot. There should be a gap (i.e. no footprinting) along the inside where your arches are. If your foot is flat, it?ll probably leave an imprint of the full bottom of your foot-no gap to be had. Your shoes may also be affected: because the ankle tilts somewhat with this condition, the heel of your shoes may become more worn on one side than another.
Diagnosis
Runners are often advised to get a gait analysis to determine what type of foot they have and so what kind of running shoe they require. This shouldn?t stop at runners. Anyone that plays sports could benefit from this assessment. Sports shoes such as football boots, astro trainers and squash trainers often have very poor arch support and so for the 60-80% of us who do overpronate or have flat feet they are left unsupported. A change of footwear or the insertion of arch support insoles or orthotics can make a massive difference to your risk of injury, to general aches and pains and even to your performance.
heelsncleavage
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have flat feet you may not necessarily need treatment -- sometimes a child or even an adult will have low arches and have no problems. It's normal for a baby's or young child's feet to appear flat until the structure of their feet is more fully developed. If flat feet are contributing to secondary problems, especially leg or foot pain, treatment may be necessary. Flat feet can sometimes cause difficulty walking or running and interfere with athletic activities. A visit to a podiatrist will involve an evaluation of foot structure and function. Besides a foot exam, a visit may include foot X-rays and an analysis of your feet while walking. Your podiatrist may prescribe arch supports or orthotics to control the pronation. While orthotics and arch supports don't permanently correct the shape of the arch, they do help control excess pronation that may be causing wear-and-tear on your muscles and joints. Sneakers with a design called motion control are also helpful for overpronators. This style of sneaker has a design that creates more stability by limiting movement in the heel and arch area of the shoe. Additionally, physical therapy and stretching exercises may be in order, especially if tendonitis (tendon inflammation) is present. Flat feet that are the result of congenital or developmental abnormalities may require further intervention, such as bracing, casting or surgical correction. A brace incorporates an arch support into a device that attaches to the lower leg, giving extra support and flat-foot control. Bracing or foot surgery may also be warranted in cases when flat feet are caused by neurological diseases or are aggravated by posterior tibial tendonitis, which can be a long-term complication of flat feet. Casting is a method used for children whose flat feet are caused by bone positional abnormalities, such as metatarsus adductus. It involves using a series of casts to assist in re-aligning leg and foot bones to their proper anatomical position.
Surgical Treatment

Surgical procedures for flat feet vary depending on the root cause of the condition. Surgical correction to control pronation may include bone implants or Achilles tendon lengthening. Tendon transfer, which is a procedure to re-attach a tendon to another area of bone, may also be used to reduce pronation and improve foot function.
All You Want To Understand About
Overview

Heel pain is a common symptom that has many possible causes. Although heel pain sometimes is caused by a systemic (body-wide) illness, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, it usually is a local condition that affects only the foot.
Causes
Some of the many causes of heel pain can include abnormal walking style (gait), such as rolling the feet inwards. Obesity. Ill-fitting shoes. Standing, running or jumping on hard surfaces. Injury to the heel, such as stress fractures. Bursitis (inflammation of a bursa, bursae are small sacs that contain fluid to lubricate moving parts, such as joints and muscles). Neuroma (nerve enlargement). Certain disorders, including diabetes and arthritis.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are pain on the bottom of the heel, pain in the arch of the foot, pain that is usually worse upon arising, pain that increases over a period of months. People with plantar fasciitis often describe the pain as worse when they get up in the morning or after they?ve been sitting for long periods of time. After a few minutes of walking the pain decreases, because walking stretches the fascia. For some people the pain subsides but returns after spending long periods of time on their feet.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist (doctor who specializes in the evaluation and treatment of foot diseases) will carry out a physical examination, and ask pertinent questions about the pain. The doctor will also ask the patient how much walking and standing the patient does, what type of footwear is worn, and details of the his/her medical history. Often this is enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes further diagnostic tests are needed, such as blood tests and imaging scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
Shoes, orthoses, splinting and/or immobilization form the cornerstone for successful functional management of plantar fasciitis.When you take the overuse nature of plantar fasciitis into account and attempt to re-establish the windlass mechanism of the foot, there is an enhanced potential for success. Unfortunately, too little attention has been directed to appropriately managing the shoes worn during treatment for plantar fasciitis. Emphasising motion control and stability type athletic shoes (that provide a firm heel cup, instep rigidity, longitudinal integrity and a well-integrated shoe upper) can help decrease excess eccentric tissue strain. The shoe also serves as a vital and functional link between an orthotic and the foot. Orthoses have long been considered to be a reliable method for treating plantar fasciitis. Considerable debate has been waged over the benefits of over-the-counter (OTC), prefabricated and prescription foot and/or ankle orthoses. Heel cushions, heel cups and cushioning pads appear to provide immediate pain relief for many people who have plantar fasciitis.This relief is frequently short-lived and requires other treatment modalities for success.Neutral position taping and strapping of the foot provides temporary symptomatic relief of pain caused by plantar fasciitis. Although the functional benefits are temporary and likely do not last longer than 10 minutes with exercise, the soft tissue compression and symptomatic relief afforded by the strapping can last for nearly a week.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
clearly adjustable heel lifts
Prevention
You should always wear footwear that is appropriate for your environment and day-to-day activities. Wearing high heels when you go out in the evening is unlikely to be harmful. However, wearing them all week at work may damage your feet, particularly if your job involves a lot of walking or standing. Ideally, you should wear shoes with laces and a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels. Do not walk barefoot on hard ground, particularly while on holiday. Many cases of heel pain occur when a person protects their feet for 50 weeks of the year and then suddenly walks barefoot while on holiday. Their feet are not accustomed to the extra pressure, which causes heel pain. If you do a physical activity, such as running or another form of exercise that places additional strain on your feet, you should replace your sports shoes regularly. Most experts recommend that sports shoes should be replaced after you have done about 500 miles in them. It is also a good idea to always stretch after exercising, and to make strength and flexibility training a part of your regular exercise routine.

Heel pain is a common symptom that has many possible causes. Although heel pain sometimes is caused by a systemic (body-wide) illness, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, it usually is a local condition that affects only the foot.
Causes
Some of the many causes of heel pain can include abnormal walking style (gait), such as rolling the feet inwards. Obesity. Ill-fitting shoes. Standing, running or jumping on hard surfaces. Injury to the heel, such as stress fractures. Bursitis (inflammation of a bursa, bursae are small sacs that contain fluid to lubricate moving parts, such as joints and muscles). Neuroma (nerve enlargement). Certain disorders, including diabetes and arthritis.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are pain on the bottom of the heel, pain in the arch of the foot, pain that is usually worse upon arising, pain that increases over a period of months. People with plantar fasciitis often describe the pain as worse when they get up in the morning or after they?ve been sitting for long periods of time. After a few minutes of walking the pain decreases, because walking stretches the fascia. For some people the pain subsides but returns after spending long periods of time on their feet.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist (doctor who specializes in the evaluation and treatment of foot diseases) will carry out a physical examination, and ask pertinent questions about the pain. The doctor will also ask the patient how much walking and standing the patient does, what type of footwear is worn, and details of the his/her medical history. Often this is enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes further diagnostic tests are needed, such as blood tests and imaging scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
Shoes, orthoses, splinting and/or immobilization form the cornerstone for successful functional management of plantar fasciitis.When you take the overuse nature of plantar fasciitis into account and attempt to re-establish the windlass mechanism of the foot, there is an enhanced potential for success. Unfortunately, too little attention has been directed to appropriately managing the shoes worn during treatment for plantar fasciitis. Emphasising motion control and stability type athletic shoes (that provide a firm heel cup, instep rigidity, longitudinal integrity and a well-integrated shoe upper) can help decrease excess eccentric tissue strain. The shoe also serves as a vital and functional link between an orthotic and the foot. Orthoses have long been considered to be a reliable method for treating plantar fasciitis. Considerable debate has been waged over the benefits of over-the-counter (OTC), prefabricated and prescription foot and/or ankle orthoses. Heel cushions, heel cups and cushioning pads appear to provide immediate pain relief for many people who have plantar fasciitis.This relief is frequently short-lived and requires other treatment modalities for success.Neutral position taping and strapping of the foot provides temporary symptomatic relief of pain caused by plantar fasciitis. Although the functional benefits are temporary and likely do not last longer than 10 minutes with exercise, the soft tissue compression and symptomatic relief afforded by the strapping can last for nearly a week.
Surgical Treatment
Although most patients with plantar fasciitis respond to non-surgical treatment, a small percentage of patients may require surgery. If, after several months of non-surgical treatment, you continue to have heel pain, surgery will be considered. Your foot and ankle surgeon will discuss the surgical options with you and determine which approach would be most beneficial for you. No matter what kind of treatment you undergo for plantar fasciitis, the underlying causes that led to this condition may remain. Therefore, you will need to continue with preventive measures. Wearing supportive shoes, stretching, and using custom orthotic devices are the mainstay of long-term treatment for plantar fasciitis.
clearly adjustable heel lifts
Prevention

You should always wear footwear that is appropriate for your environment and day-to-day activities. Wearing high heels when you go out in the evening is unlikely to be harmful. However, wearing them all week at work may damage your feet, particularly if your job involves a lot of walking or standing. Ideally, you should wear shoes with laces and a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels. Do not walk barefoot on hard ground, particularly while on holiday. Many cases of heel pain occur when a person protects their feet for 50 weeks of the year and then suddenly walks barefoot while on holiday. Their feet are not accustomed to the extra pressure, which causes heel pain. If you do a physical activity, such as running or another form of exercise that places additional strain on your feet, you should replace your sports shoes regularly. Most experts recommend that sports shoes should be replaced after you have done about 500 miles in them. It is also a good idea to always stretch after exercising, and to make strength and flexibility training a part of your regular exercise routine.
Trendelenburg Gait Leg Length Discrepancy
Overview
People with leg length discrepancy, when one leg is longer than the other, usually have a waddling-type gait where the hips seem to move up and down during walking as the body tries to compensate for the inequality. There are two types of leg length discrepancy. The first type of leg length discrepancy involves a structural defect, where one bone is longer or shorter than the corresponding bone of the other limb. This can occur within the femur (upper leg bone) or the tibia and fibular (lower leg bones). Functional leg length discrepancy results from altered mechanics due to a malalignment in the spine or lower extremity.
Causes
Leg length discrepancies can be caused by poor alignment of the pelvis or simply because one leg is structurally longer than the other. Regardless of the reason, your body wants to be symmetrical and will do its best to compensate for the length difference. The greater the leg length difference, the earlier the symptoms will present themselves to the patient. Specific diagnoses that coincide with leg length discrepancy include: scoliosis, lumbar herniated discs, sacroiliitis, pelvic obiliquity, greater trochanteric bursitis, hip arthritis, piriformis syndrome, patellofemoral syndrome and foot pronation. Other potential causes could be due to an injury (such as a fracture), bone disease, bone tumors, congenital problems (present at birth) or from a neuromuscular problem.
Symptoms
Many people walk around with LLD?s of up to 2 cm. and not even know it. However, discrepancies above 2 cm. becomes more noticeable, and a slight limp is present. But even up to 3 cm. a small lift compensates very well, and many patients are quite happy with this arrangement. Beyond 3 cm. however, the limp is quite pronounced, and medical care is often sought at that point. Walking with a short leg gait is not only unsightly, but increases energy expenditure during ambulation. It could also put more stress on the long leg, and causes functional scoliosis. Where the discrepancy is more severe, walking becomes grotesque or virtually impossible.
Diagnosis
On standing examination one iliac crest may be higher/lower than the other. However a physiotherapist, osteopath or chiropractor will examine the LLD in prone or supine position and measure it, confirming the diagnosis of structural (or functional) LLD. The LLD should be measured using bony fixed points. X-Ray should be taken in a standing position. The osteopath, physiotherapist or chiropractor will look at femoral head & acetabulum, knee joints, ankle joints.
Non Surgical Treatment
To begin a path torwards a balanced foundation and reduce pain from leg length discrepancy, ask your doctor about these Functional Orthotics and procedures. Functional Orthotics have been shown to specifically reduce pain from leg length inequality, support all three arches of the foot to create a balanced foundation, maximize shock absorption, add extra propulsion, and supply more stability, enable posture correction and long-term preventive protection. Will improve prolonged effectiveness of chiropractic adjustments. Shoe or heel Lifts, Correct the deficiencies that causes imbalances in the body.

how to increase height naturally after 21
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatments vary in complexity. Sometimes the goal of surgery is to stop the growth of the longer limb. Other times, surgeons work to lengthen the shorter limb. Orthopedic surgeons may treat children who have limb-length conditions with one or a combination of these surgical techniques. Bone resection. An operation to remove a section of bone, evening out the limbs in teens or adults who are no longer growing. Epiphyseal stapling. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by inserting staples into the growth plate, then removing them when the desired result is achieved. Epiphysiodesis. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by creating a permanent bony ridge near the growth plate. Limb lengthening. A procedure (also called distraction osteogenesis or the Ilizarov procedure) that involves attaching an internal or external fixator to a limb and gradually pulling apart bone segments to grow new bone between them. There are several ways your doctor can predict the final LLD, and thus the timing of the surgery. The easiest way is the so-called Australian method, popularised by Dr. Malcolm Menelaus, an Australian orthopedic surgeon. According to this method, growth in girls is estimated to stop at age 14, and in boys at age 16 years. The femur grows at the rate of 10 mm. a year, and the upper tibia at the rate of 6 mm. a year. Using simple arithmetic, one can get a fairly good prediction of future growth. This of course, is an average, and the patient may be an average. To cut down the risk of this, the doctor usually measures leg length using special X-ray technique (called a Scanogram) on three occasions over at least one year duration to estimate growth per year. He may also do an X-ray of the left hand to estimate the bone age (which in some cases may differ from chronological age) by comparing it with an atlas of bone age. In most cases, however, the bone age and chronological age are quite close. Another method of predicting final LLD is by using Anderson and Green?s remaining growth charts. This is a very cumbersome method, but was till the 1970?s, the only method of predicting remaining growth. More recently, however, a much more convenient method of predicting LLD was discovered by Dr. Colin Moseley from Montreal. His technique of using straight line graphs to plot growth of leg lengths is now the most widely used method of predicting leg length discrepancy. Whatever method your doctor uses, over a period of one or two years, once he has a good idea of the final LLD, he can then formulate a plan to equalize leg lengths. Epiphyseodesis is usually done in the last 2 to 3 years of growth, giving a maximum correction of about 5 cm. Leg lengthening can be done at any age, and can give corrections of 5 to10 cm., or more.
People with leg length discrepancy, when one leg is longer than the other, usually have a waddling-type gait where the hips seem to move up and down during walking as the body tries to compensate for the inequality. There are two types of leg length discrepancy. The first type of leg length discrepancy involves a structural defect, where one bone is longer or shorter than the corresponding bone of the other limb. This can occur within the femur (upper leg bone) or the tibia and fibular (lower leg bones). Functional leg length discrepancy results from altered mechanics due to a malalignment in the spine or lower extremity.

Causes
Leg length discrepancies can be caused by poor alignment of the pelvis or simply because one leg is structurally longer than the other. Regardless of the reason, your body wants to be symmetrical and will do its best to compensate for the length difference. The greater the leg length difference, the earlier the symptoms will present themselves to the patient. Specific diagnoses that coincide with leg length discrepancy include: scoliosis, lumbar herniated discs, sacroiliitis, pelvic obiliquity, greater trochanteric bursitis, hip arthritis, piriformis syndrome, patellofemoral syndrome and foot pronation. Other potential causes could be due to an injury (such as a fracture), bone disease, bone tumors, congenital problems (present at birth) or from a neuromuscular problem.
Symptoms
Many people walk around with LLD?s of up to 2 cm. and not even know it. However, discrepancies above 2 cm. becomes more noticeable, and a slight limp is present. But even up to 3 cm. a small lift compensates very well, and many patients are quite happy with this arrangement. Beyond 3 cm. however, the limp is quite pronounced, and medical care is often sought at that point. Walking with a short leg gait is not only unsightly, but increases energy expenditure during ambulation. It could also put more stress on the long leg, and causes functional scoliosis. Where the discrepancy is more severe, walking becomes grotesque or virtually impossible.
Diagnosis
On standing examination one iliac crest may be higher/lower than the other. However a physiotherapist, osteopath or chiropractor will examine the LLD in prone or supine position and measure it, confirming the diagnosis of structural (or functional) LLD. The LLD should be measured using bony fixed points. X-Ray should be taken in a standing position. The osteopath, physiotherapist or chiropractor will look at femoral head & acetabulum, knee joints, ankle joints.
Non Surgical Treatment
To begin a path torwards a balanced foundation and reduce pain from leg length discrepancy, ask your doctor about these Functional Orthotics and procedures. Functional Orthotics have been shown to specifically reduce pain from leg length inequality, support all three arches of the foot to create a balanced foundation, maximize shock absorption, add extra propulsion, and supply more stability, enable posture correction and long-term preventive protection. Will improve prolonged effectiveness of chiropractic adjustments. Shoe or heel Lifts, Correct the deficiencies that causes imbalances in the body.

how to increase height naturally after 21
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatments vary in complexity. Sometimes the goal of surgery is to stop the growth of the longer limb. Other times, surgeons work to lengthen the shorter limb. Orthopedic surgeons may treat children who have limb-length conditions with one or a combination of these surgical techniques. Bone resection. An operation to remove a section of bone, evening out the limbs in teens or adults who are no longer growing. Epiphyseal stapling. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by inserting staples into the growth plate, then removing them when the desired result is achieved. Epiphysiodesis. An operation to slow the rate of growth of the longer limb by creating a permanent bony ridge near the growth plate. Limb lengthening. A procedure (also called distraction osteogenesis or the Ilizarov procedure) that involves attaching an internal or external fixator to a limb and gradually pulling apart bone segments to grow new bone between them. There are several ways your doctor can predict the final LLD, and thus the timing of the surgery. The easiest way is the so-called Australian method, popularised by Dr. Malcolm Menelaus, an Australian orthopedic surgeon. According to this method, growth in girls is estimated to stop at age 14, and in boys at age 16 years. The femur grows at the rate of 10 mm. a year, and the upper tibia at the rate of 6 mm. a year. Using simple arithmetic, one can get a fairly good prediction of future growth. This of course, is an average, and the patient may be an average. To cut down the risk of this, the doctor usually measures leg length using special X-ray technique (called a Scanogram) on three occasions over at least one year duration to estimate growth per year. He may also do an X-ray of the left hand to estimate the bone age (which in some cases may differ from chronological age) by comparing it with an atlas of bone age. In most cases, however, the bone age and chronological age are quite close. Another method of predicting final LLD is by using Anderson and Green?s remaining growth charts. This is a very cumbersome method, but was till the 1970?s, the only method of predicting remaining growth. More recently, however, a much more convenient method of predicting LLD was discovered by Dr. Colin Moseley from Montreal. His technique of using straight line graphs to plot growth of leg lengths is now the most widely used method of predicting leg length discrepancy. Whatever method your doctor uses, over a period of one or two years, once he has a good idea of the final LLD, he can then formulate a plan to equalize leg lengths. Epiphyseodesis is usually done in the last 2 to 3 years of growth, giving a maximum correction of about 5 cm. Leg lengthening can be done at any age, and can give corrections of 5 to10 cm., or more.
Addressing Mortons Neuroma
Overview
 Morton?s neuroma occurs as the nerve passes under the ligament connecting the toe bones (metatarsals) in the forefoot. Morton?s neuroma most frequently develops between the third and fourth toes, usually in response to irritation, trauma or excessive pressure. The incidence of Morton?s neuroma is 8 to 10 times greater in women than in men.
Morton?s neuroma occurs as the nerve passes under the ligament connecting the toe bones (metatarsals) in the forefoot. Morton?s neuroma most frequently develops between the third and fourth toes, usually in response to irritation, trauma or excessive pressure. The incidence of Morton?s neuroma is 8 to 10 times greater in women than in men.
Causes
Inappropriate footwear is one of the principle causes of Morton?s neuroma. Toe spring and tapering toe boxes are the most problematic shoe design features that contribute to this health problem. Morton?s neuroma occurs when one of your nerves is stretched and pinched, which happens with great frequency in people who wear shoes incorporating these design features. A professional shoe fitting should always be sought if you are struggling with neuroma-related symptoms.
Symptoms
If you have a Morton?s neuroma, you may have one or more of these symptoms where the nerve damage is occurring, Tingling, burning, or numbness, pain, a feeling that something is inside the ball of the foot or a feeling that there?s something in the shoe or a sock is bunched up. The progression of a Morton?s neuroma often follows the following pattern. The symptoms begin gradually. At first they occur only occasionally, when wearing narrow-toed shoes or performing certain aggravating activities. The symptoms may go away temporarily by removing the shoe, massaging the foot, or by avoiding aggravating shoes or activities. Over time the symptoms progressively worsen and may persist for several days or weeks. The symptoms become more intense as the neuroma enlarges and the temporary changes in the nerve become permanent.
Diagnosis
During the examination, your physician will feel for a palpable mass or a "click" between the bones. He or she will put pressure on the spaces between the toe bones to try to replicate the pain and look for calluses or evidence of stress fractures in the bones that might be the cause of the pain. Range of motion tests will rule out arthritis or joint inflammations. X-rays may be required to rule out a stress fracture or arthritis of the joints that join the toes to the foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
Pain is the main reason that you seek treatment for a neuroma. Analgesics may help. Inflammation it best eased via ice therapy and techniques or exercises that deload the inflammed structures. Anti-inflammatory medications may help. Your physiotherapist will use an array of treatment tools to reduce your pain and inflammation. These include: ice, electrotherapy, acupuncture, deloading taping techniques, soft tissue massage and orthotics to offload the irritated nerve. One of the biggest factors in relieving pain may be changing or modifying your footwear. This may mean adding felt, foam or gel products to your shoe to help offload the area, or looking at avoiding tight fitting heels or shoes.
Surgical Treatment
Recently, an increasing number of procedures are being performed at specialist centers under radiological or ultrasound guidance. Recent studies have shown excellent results for the treatment of Morton's neuroma with ultrasound guided steroid injections, ultrasound guided sclerosing alcohol injections, ultrasound guided radiofrequency ablation and ultrasound guided cryo-ablation.
Causes
Inappropriate footwear is one of the principle causes of Morton?s neuroma. Toe spring and tapering toe boxes are the most problematic shoe design features that contribute to this health problem. Morton?s neuroma occurs when one of your nerves is stretched and pinched, which happens with great frequency in people who wear shoes incorporating these design features. A professional shoe fitting should always be sought if you are struggling with neuroma-related symptoms.
Symptoms
If you have a Morton?s neuroma, you may have one or more of these symptoms where the nerve damage is occurring, Tingling, burning, or numbness, pain, a feeling that something is inside the ball of the foot or a feeling that there?s something in the shoe or a sock is bunched up. The progression of a Morton?s neuroma often follows the following pattern. The symptoms begin gradually. At first they occur only occasionally, when wearing narrow-toed shoes or performing certain aggravating activities. The symptoms may go away temporarily by removing the shoe, massaging the foot, or by avoiding aggravating shoes or activities. Over time the symptoms progressively worsen and may persist for several days or weeks. The symptoms become more intense as the neuroma enlarges and the temporary changes in the nerve become permanent.
Diagnosis
During the examination, your physician will feel for a palpable mass or a "click" between the bones. He or she will put pressure on the spaces between the toe bones to try to replicate the pain and look for calluses or evidence of stress fractures in the bones that might be the cause of the pain. Range of motion tests will rule out arthritis or joint inflammations. X-rays may be required to rule out a stress fracture or arthritis of the joints that join the toes to the foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
Pain is the main reason that you seek treatment for a neuroma. Analgesics may help. Inflammation it best eased via ice therapy and techniques or exercises that deload the inflammed structures. Anti-inflammatory medications may help. Your physiotherapist will use an array of treatment tools to reduce your pain and inflammation. These include: ice, electrotherapy, acupuncture, deloading taping techniques, soft tissue massage and orthotics to offload the irritated nerve. One of the biggest factors in relieving pain may be changing or modifying your footwear. This may mean adding felt, foam or gel products to your shoe to help offload the area, or looking at avoiding tight fitting heels or shoes.

Surgical Treatment
Recently, an increasing number of procedures are being performed at specialist centers under radiological or ultrasound guidance. Recent studies have shown excellent results for the treatment of Morton's neuroma with ultrasound guided steroid injections, ultrasound guided sclerosing alcohol injections, ultrasound guided radiofrequency ablation and ultrasound guided cryo-ablation.
Shoe Lifts For Leg Length Discrepancy
There are two different types of leg length discrepancies, congenital and acquired. Congenital means you are born with it. One leg is anatomically shorter than the other. Through developmental stages of aging, the brain picks up on the step pattern and recognizes some variation. The entire body usually adapts by dipping one shoulder to the "short" side. A difference of less than a quarter inch is not really irregular, demand Shoe Lifts to compensate and usually does not have a serious effect over a lifetime.

Leg length inequality goes largely undiagnosed on a daily basis, yet this problem is simply corrected, and can reduce many incidents of lower back pain.
Therapy for leg length inequality usually consists of Shoe Lifts. These are typically very reasonably priced, normally priced at under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back pain is easily the most prevalent ailment affecting people today. Over 80 million people experience back pain at some point in their life. It is a problem that costs employers millions each year because of time lost and production. Fresh and more effective treatment methods are always sought after in the hope of reducing the economical impact this condition causes.

People from all corners of the earth experience foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these types of situations Shoe Lifts might be of worthwhile. The lifts are capable of relieving any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless experienced orthopaedic physicians.
In order to support the human body in a well-balanced manner, your feet have a significant role to play. In spite of that, it's often the most overlooked area of the human body. Many people have flat-feet which means there may be unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other body parts such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that proper posture and balance are restored.

Leg length inequality goes largely undiagnosed on a daily basis, yet this problem is simply corrected, and can reduce many incidents of lower back pain.
Therapy for leg length inequality usually consists of Shoe Lifts. These are typically very reasonably priced, normally priced at under twenty dollars, in comparison to a custom orthotic of $200 plus. Differences over a quarter inch can take their toll on the spine and should probably be compensated for with a heel lift. In some cases, the shortage can be so extreme that it requires a full lift to both the heel and sole of the shoe.
Back pain is easily the most prevalent ailment affecting people today. Over 80 million people experience back pain at some point in their life. It is a problem that costs employers millions each year because of time lost and production. Fresh and more effective treatment methods are always sought after in the hope of reducing the economical impact this condition causes.

People from all corners of the earth experience foot ache due to leg length discrepancy. In these types of situations Shoe Lifts might be of worthwhile. The lifts are capable of relieving any pain and discomfort in the feet. Shoe Lifts are recommended by countless experienced orthopaedic physicians.
In order to support the human body in a well-balanced manner, your feet have a significant role to play. In spite of that, it's often the most overlooked area of the human body. Many people have flat-feet which means there may be unequal force placed on the feet. This will cause other body parts such as knees, ankles and backs to be impacted too. Shoe Lifts make sure that proper posture and balance are restored.
The Best Way To Protect Against Calcaneal Spur

Overview
A common cause of heel pain is the heel spur, which is a bony growth on the underside of the heel bone. The spur, visible by X-ray, appears as a protrusion that can extend forward as much as half an inch. When there is no indication of bone enlargement, the condition is sometimes referred to as ?heel spur syndrome.?
Heel spurs result from strain on the muscles and ligaments of the foot, by stretching of the long band of tissue that connects the heel and the ball of the foot, and by repeated tearing away of the lining or membrane that covers the heel bone. These conditions may result from biomechanical imbalance, running or jogging, improperly fitted or excessively worn shoes, or obesity. Heel spurs specifically relate to the bony spurs (extra bony growth) that form at the base of the heel. It is a ?spike? of bone that grows from the base of the heel.
Causes
At the onset of this condition, pain and swelling become present, with discomfort particularly noted as pushing off with the toes occurs during walking. This movement of the foot stretches the fascia that is already irritated and inflamed. If this condition is allowed to continue, pain is noticed around the heel region because of the newly formed bone, in response to the stress. This results in the development of the heel spur. It is common among athletes and others who run and jump a significant amount.
Symptoms
Heel spurs can be quite painful, but can just as likely occur with no symptoms at all. Plantar fasciitis is a contributing condition to heel spurs. The cause of the pain is not the heel spur itself but the soft-tissue injury associated with it. The feeling has been described as a knife or pin sticking into the bottom of your feet when you first stand up after sitting or laying down for a long period of time - a pain that later turns into a dull ache.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a heel spur can be done with an x-ray, which will be able to reveal the bony spur. Normally, it occurs where the plantar fascia connects to the heel bone. When the plantar fascia ligament is pulled excessively it begins to pull away from the heel bone. When this excessive pulling occurs, it causes the body to respond by depositing calcium in the injured area, resulting in the formation of the bone spur. The Plantar fascia ligament is a fibrous band of connective tissue running between the heel bone and the ball of the foot. This structure maintains the arch of the foot and distributes weight along the foot as we walk. However, due to the stress that this ligament must endure, it can easily become damaged which commonly occurs along with heel spurs.
Non Surgical Treatment
Exercise. If you think your pain is exercise-related, change your exercise routine, environment, or foot-ware, and emphasize movements and/or body parts that do not cause pain. Mind/Body. Occasionally foot pain can be related to stress. The body may respond with generalized tension that contributes to pain in many areas, including the feet. Hypnosis and guided imagery are worth exploring if an anatomical problem is not apparent. Supplements. Natural anti-inflammatories can be just as effective as ibuprofen or other over-the-counter pain relievers with fewer side effects. Try one of the following. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) standardized to 5-6% gingerols and 6% shogoals, take one to two 500 mg tablets three to four times daily. Turmeric (Curcuma longa) standardized to 95% curcuminoids, take 400-600 mg three times daily. Also, be sure that you're wearing well-fitting shoes, the proper shoes for each activity, and that you buy new foot-ware as soon as you notice signs of wear. You can also take the pressure off your heel with a donut-shaped heel cushion or a heel-raising pad placed in your shoe. Acupuncture can also relieve the pain, as can for some sufferers, magnetic shoe inserts, although the evidence behind their effectiveness is not conclusive. Osteopathic or chiropractic manipulation can help with soft tissue pain in and around the feet.
Surgical Treatment
Though conservative treatments for heel spurs work most of the time, there are some cases where we need to take your treatment to the next level. Luckily, with today?s technologies, you can still often avoid surgery. Some of the advanced technologies to treat a Heel Spur are Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy. Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy (also known as PRP) is one of several regenerative medicine techniques that University Foot and Ankle Institute has helped bring to foot and ankle care. This amazing in-office procedure allows the growth factors in the blood to be used to actually begin the healing process again long after your body has given up on healing the area. Heel Pain Shockwave Therapy. Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive procedure done in the office that allows for new blood to get to the region of fascia damage and help with healing. Results have been excellent with more than 70 percent of patients getting relief with only one treatment. Topaz for Heal Spurs and pain. Another minimally invasive technology technique is called Coblation Surgery using a Topaz probe. This minimally invasive procedure involves controlled heating of multiple tiny needles that are inserted through the skin and into the plantar fascia. This process, like PRP and Shockwave therapy, irritates the fascia enough to turn a chronic problem back into an acute problem, greatly increasing the chances of healing. Heel Spur Surgery. Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy is one surgical procedure that we consider to release the tight fascia. University Foot and Ankle Institute has perfected an endoscopic (camera guided) approach for fascia release to allow rapid healing and limited downtime with minimal pain.
Prevention
A variety of steps can be taken to avoid heel pain and accompanying afflictions. Wear shoes that fit well-front, back, and sides-and have shock-absorbent soles, rigid shanks, and supportive heel counters. Wear the proper shoes for each activity. Do not wear shoes with excessive wear on heels or soles. Prepare properly before exercising. Warm up and do stretching exercises before and after running. Pace yourself when you participate in athletic activities. Don't underestimate your body's need for rest and good nutrition. If obese, lose weight.
What Is A Calcaneal Spur
Overview
Bone spurs including heel spurs occur as a natural response of the body to wear and tear. Heel spur in particular, can cause pain when it rubs against soft tissues including the Achilles tendon. When that happens movement can become restricted. Spurs can also appear in other joint areas such as under the toenail where it would lead to pain and nail deformation.
Causes
When the Plantar Fascia is allowed to rest during sleep or long periods of inactivity, the fascia tightens and shortens. When you first stand up after resting, the fascia is forced to stretch very quickly causing micro-tears in the tissue. This is why the first steps in the morning are so exquisitely painful. Heel spurs are more likely to happen if you suffer from over-pronation (walking with a rolling gait) you stand or walk on rigid surfaces for long periods, you are above ideal weight or during pregnancy, you have stiff muscles in your calves.

Symptoms
You'll typically first notice early heel spur pain under your heel in the morning or after resting. Your heel pain will be worse with the first steps and improves with activity as it warms up. When you palpate the tender area you may feel a tender bony lump. As your plantar fasciitis deteriorates and your heel spur grows, the pain will be present more often.
Diagnosis
Because the diagnosis of heel spurs can be confused with tarsal tunnel syndrome (as described earlier), most surgeons advocate performing a tarsal tunnel release (or at least a partial tarsal tunnel release) along with the plantar fascia release. This surgery is about 80percent successful in relieving pain in the small group of patients who do not improve with conservative treatments.
Non Surgical Treatment
The majority of heel spurs are treated with non-surgical interventions. These can relieve pain, but may take from about 3 months to up to a year for symptoms to resolve. Rest, icing, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory or prescription medications can help ease symptoms. Cortisone injections may also be used. Physical therapists may instruct you to perform stretching exercises to help relax the tissues in the heel. Your doctor may recommend custom orthotics or shoe inserts to position and cushion your heel. Night splints can help position the heel and arch of the foot while you sleep. Some doctors may recommend extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT). This treatment uses energy pulses to start the repair process in the heel tissues. ESWT is recommend when other non-surgical treatments have failed.
Surgical Treatment
Usually, heel spurs are curable with conservative treatment. If not, heel spurs are curable with surgery, although there is the possibility of them growing back. About 10% of those who continue to see a physician for plantar fascitis have it for more than a year. If there is limited success after approximately one year of conservative treatment, patients are often advised to have surgery.
Prevention
o help prevent heel and bone spurs, wear properly designed and fitted shoes or boots that provide sufficient room in the toe box so as not to compress the toes. They should also provide cushioning in appropriate areas to minimize the possibility of the irritation and inflammation that can lead to bone spurs in the feet. If needed, use inserts that provide arch support and a slight heel lift to help ensure that not too much stress is placed on the plantar fascia. This helps to reduce the possibility of inflammation and overstress. Wearing padded socks can also help by reducing trauma. Peer-reviewed, published studies have shown that wearing clinically-tested padded socks can help protect against injuries to the skin/soft tissue of the foot due to the effects of impact, pressure and shear forces. Also consider getting your gait analyzed by a foot health professional for appropriate orthotics. If you have heel pain, toe pain or top-of-the-foot pain, see your doctor or foot specialist to ensure that a spur has not developed.